Corneal Cross-Linking
Corneal Cross-Linking – Treatment for Keratoconus
What is Keratoconus?
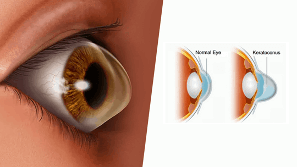
Keratoconus is a degenerative disease that affects the cornea. The cornea is the clear, domelike structure that helps focus light rays to the back of the eye. The cornea can be described as “the front window of the eye.” Keratoconus causes the collagen bonds that help maintain the cornea’s shape and rigidity to weaken, which ultimately leads to the progressive “coning” of the cornea. This change in shape can create visual distortions like increased nearsightedness and astigmatism. If left untreated, keratoconus may progress to the point where a cornea transplant is needed. Fortunately, with advancing technology, there are new treatment methods that can help stop the progression of keratoconus and in some cases help improve vision.
Corneal Cross-linking (CXL)
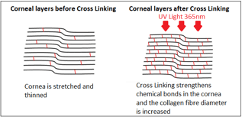
Corneal Cross-linking is one of the latest advancements in treatment for people with keratoconus. Cross-linking is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a combination of riboflavin (vitamin B2) drops and UV (ultraviolet) light to help increase the bonds between the collagen fibers in the cornea. This process will allow the cornea to maintain its shape and slow or stop the progressive “coning” of the cornea associated with keratoconus.
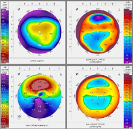
Your doctor will complete a very thorough eye exam along with advanced corneal imaging and topography to determine if you are a candidate for cross-linking.
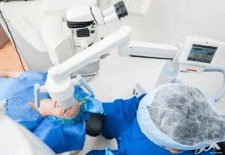
The treatment typically takes around one hour. Your doctor may provide you with a medication to relax you and numbing drops in your eyes. You will be awake during the treatment and patients typically experience no pain or discomfort during the procedure. You will be required to be cautious and not rub or touch your eyes for brief period after your procedure to be determined by your doctor. Please contact us to learn more about your treatment option with corneal cross-linking.



